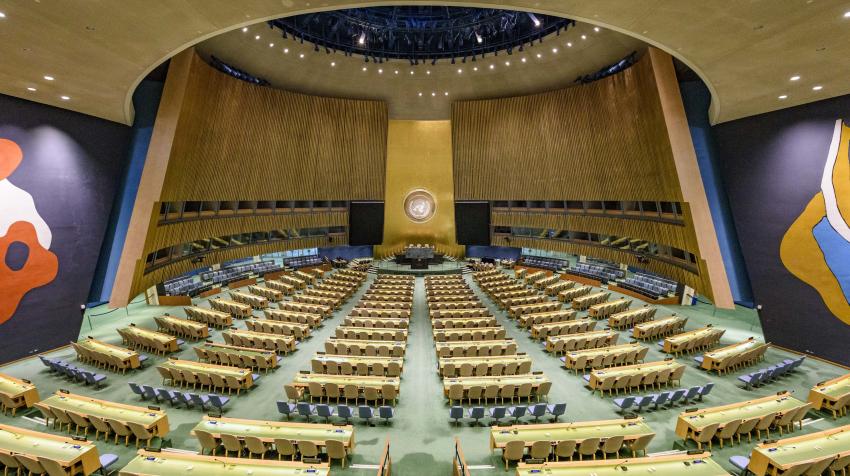
On October 24, 1945, in the immediate aftermath of the devastating Second World War, the United Nations (UN) officially came into existence. This pivotal moment marked the culmination of years of planning and negotiation, signaling a global commitment to peace, cooperation, and the prevention of future world conflicts.
The Charter and the Core Mission
The UN was established following the ratification of the founding document, the UN Charter, by a majority of the 51 initial member states, including the five permanent members of the Security Council: China, France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
The Charter outlines the organization’s four main purposes:
- To maintain international peace and security.
- To develop friendly relations among nations.
- To achieve international cooperation in solving global problems.
- To be a center for harmonizing the actions of nations in the attainment of these common ends.
The structure of the UN was designed to be stronger and more effective than its predecessor, the League of Nations, which had failed to prevent the outbreak of WWII.
From San Francisco to Global Institution
The foundation for the UN was laid earlier that year at the San Francisco Conference, where delegates from 50 nations met from April to June 1945 to draft the Charter.
When the Charter entered into force on October 24, 1945, this date was designated as United Nations Day, and it is celebrated annually to recognize the work and achievements of the organization. Today, the UN has grown into a vast global body with 193 member states, working on issues ranging from human rights and sustainable development to global health and humanitarian aid. The founding date remains a profound reminder of the international resolve to build a better, more peaceful future from the ashes of war.
The 51 Founding Nations of the United Nations:
Here is the list of the original 51 member states that signed the Declaration by United Nations in 1942 or participated in the San Francisco Conference in 1945 and signed the UN Charter:
- Argentina
- Australia
- Belgium
- Bolivia
- Brazil
- Byelorussian S.S.R. (Belarus)
- Canada
- Chile
- China
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Czechoslovakia
- Denmark
- Dominican Republic
- Ecuador
- Egypt
- El Salvador
- Ethiopia
- France
- Greece
- Guatemala
- Haiti
- Honduras
- India
- Iran
- Iraq
- Lebanon
- Liberia
- Luxembourg
- Mexico
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Nicaragua
- Norway
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Philippines
- Poland
- Saudi Arabia
- Syria
- Turkey
- Ukrainian S.S.R. (Ukraine)
- Union of South Africa
- Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Russia)
- United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- United States of America
- Uruguay
- Venezuela
- Yugoslavia
Sign up for our Sunday Spectator. Delivered to your inbox every Sunday, with all the news from the week.